Using JSON Web Tokens with Laravel to create APIs
Using JWT to authenticate users through APIs is especially useful since it does not require implementing sessions on the server and the JWT itself contains the information corresponding to the user making the request, which serves to validate their authenticity.
First of all, we need to install Laravel and create a project. Instructions to install Laravel 5.8. After having Laravel installed, we proceed to create a project.
$ laravel new webpageTo implement JWT in Laravel we will use the module called tymondesigns/jwt-auth with the following code:
$ composer require tymon/jwt-auth:dev-develop --prefer-sourceThen to generate the configuration file we run the following code:
$ php artisan vendor:publish --provider="Tymon\JWTAuth\Providers\LaravelServiceProvider"We proceed to generate a key for our project:
$ php artisan jwt:secretFor Laravel to automatically connect to our database and use it as a user validation method, we must create a users table with the following columns:
idPRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENTnameVARCHARsurnameVARCHARemailVARCHARpasswordVARCHARcreate_atTIMESTAMPupdated_atTIMESTAMP
The User model will use the users table by default. If you want to specify another name for the table, you can define the name to use in app\User.php with the following code:
...
protected $table = ''; // we put the table name
...The following steps are at the code level. We need to implement Tymon\JWTAuth\Contracts\JWTSubject in the User model. In this model we must implement two methods: getJWTIdentifier() and getJWTCustomClaims().
The User model in app\User.php should look similar to this:
<?php
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Notifications\Notifiable;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Auth\MustVerifyEmail;
use Tymon\JWTAuth\Contracts\JWTSubject;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Auth\User as Authenticatable;
class User extends Authenticatable implements JWTSubject {
use Notifiable;
protected $fillable = [
'name', 'surname', 'email', 'password',
];
protected $hidden = [
'password', 'remember_token',
];
protected $casts = [
'email_verified_at' => 'datetime',
];
public function getJWTIdentifier() {
return $this->getKey();
}
public function getJWTCustomClaims() {
return [];
}
}Now for Laravel to use JWT as an authentication method, we open the config/auth.php file and modify the following data:
'defaults' => [
'guard' => 'api',
'passwords' => 'users',
],
...
'guards' => [
'api' => [
'driver' => 'jwt',
'provider' => 'users',
],
],Now we proceed to add the authentication controller. We will call it AuthController. We can create it manually or with the following command:
$ php artisan make:controller AuthControllerIn this controller we put the following code:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Http\Requests\RegisterAuthRequest;
use App\User;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use JWTAuth;
use Tymon\JWTAuth\Exceptions\JWTException;
class AuthController extends Controller {
public $loginAfterSignUp = true;
public function register(Request $request) {
$user = new User();
$user->name = $request->name;
$user->surname = $request->surname;
$user->email = $request->email;
$user->password = bcrypt($request->password);
$user->save();
if ($this->loginAfterSignUp) {
return $this->login($request);
}
return response()->json([
'status' => 'ok',
'data' => $user
], 200);
}
public function login(Request $request) {
$input = $request->only('email', 'password');
$jwt_token = null;
if (!$jwt_token = JWTAuth::attempt($input)) {
return response()->json([
'status' => 'invalid_credentials',
'message' => 'Incorrect email or password.',
], 401);
}
return response()->json([
'status' => 'ok',
'token' => $jwt_token,
]);
}
public function logout(Request $request) {
$this->validate($request, [
'token' => 'required'
]);
try {
JWTAuth::invalidate($request->token);
return response()->json([
'status' => 'ok',
'message' => 'Logout successful.'
]);
} catch (JWTException $exception) {
return response()->json([
'status' => 'unknown_error',
'message' => 'The user could not be logged out.'
], 500);
}
}
public function getAuthUser(Request $request) {
$this->validate($request, [
'token' => 'required'
]);
$user = JWTAuth::authenticate($request->token);
return response()->json(['user' => $user]);
}
}Now we create the routes that will access these methods in routes\api.php:
<?php
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
// these routes can be accessed without providing a valid token.
Route::post('/login', 'AuthController@login');
Route::post('/register', 'AuthController@register');
// these routes require a valid token to be accessed.
Route::group(['middleware' => 'auth.jwt'], function () {
Route::post('/logout', 'AuthController@logout');
});Additionally, we can add the following code at the beginning of public\index.php to avoid CORS errors during our tests:
// allows requests from any origin
header('Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *');
// allows requests with GET, PUT, POST, DELETE and OPTIONS methods
header('Access-Control-Allow-Methods: GET, PUT, POST, DELETE, OPTIONS');
// allows the Content-Type and Authorization headers
header('Access-Control-Allow-Headers: Content-Type, Authorization');This concludes the configuration part of Laravel to use JSON Web Tokens. Now we proceed to make some test requests using Insomnia to verify that our routes are working.
We make a request to the /api/register route and confirm that we receive a status: ok and a token.
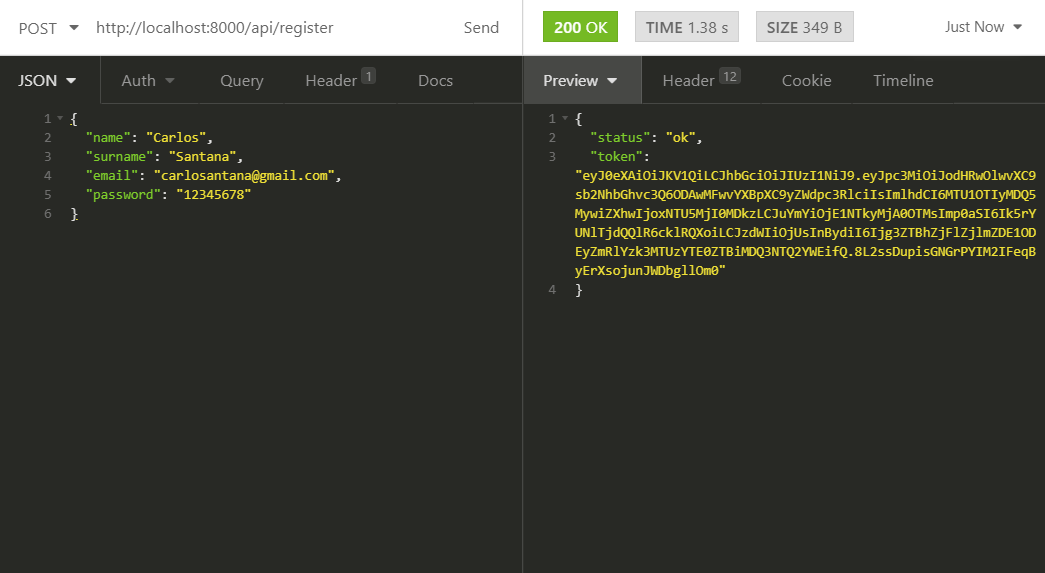
This means that this user was registered in the database and a token was automatically generated that we must send with each request to protected routes.
We can also test /api/login.
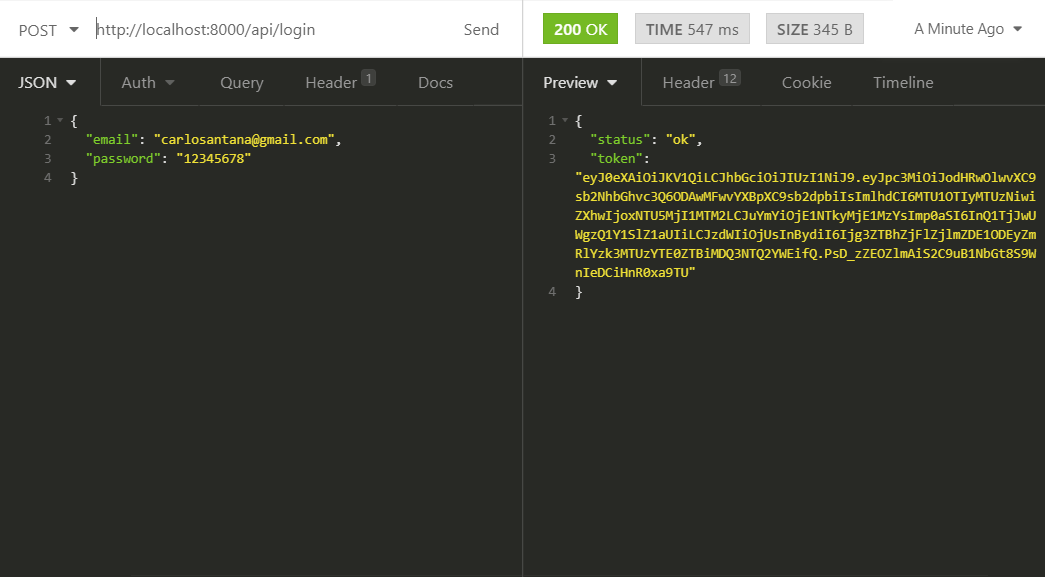
The token can be sent in each request in different ways:
- We can do it by url in the case of using
GETfor example.../api/products?token=eyJ0eXAiOiJ.... - As a property of a JSON sent in a
POST. - Or as part of the
Authorization: Bearer eyJ0eXAiOiJ...header.
In the following example we send it as a property in a JSON to log out the user using api/logout.
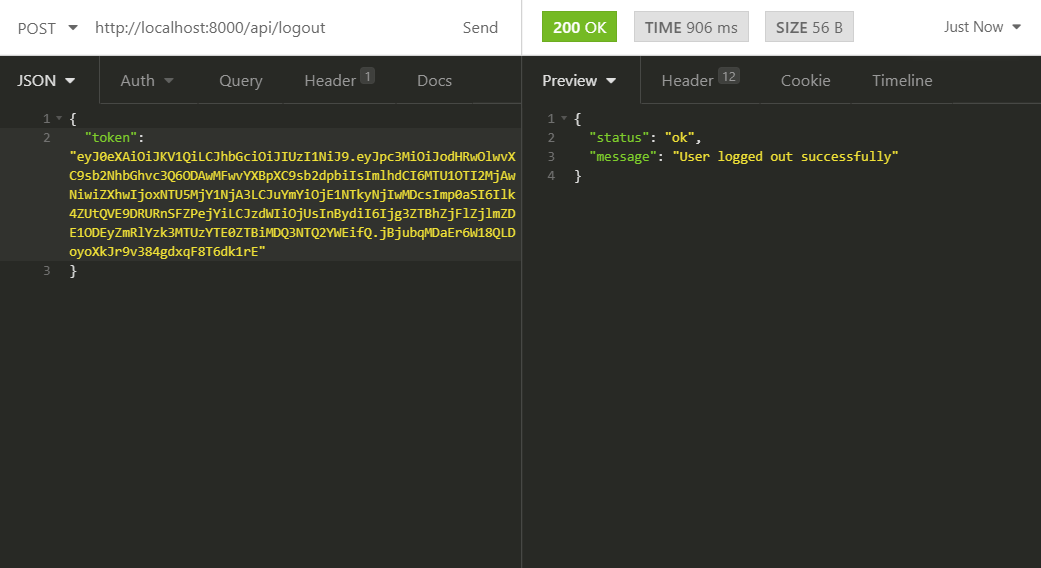
In the same way we could continue creating more protected routes which would require a valid token to be accessed. As always, any questions can be left in the comments. Regards.

